|
22 Kalliope
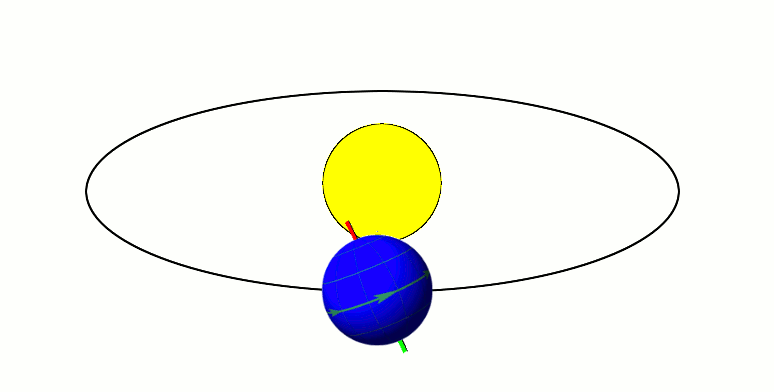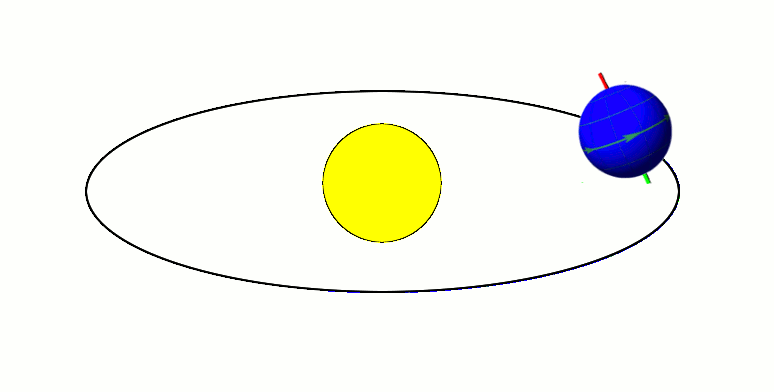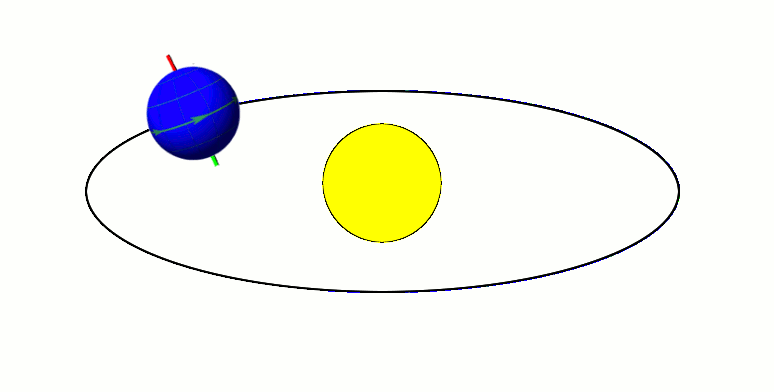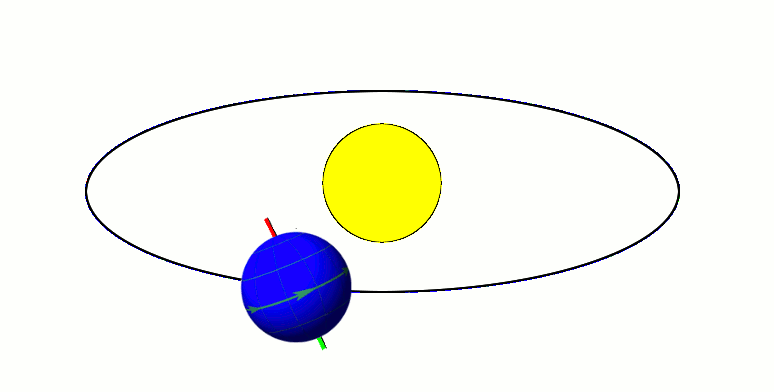
Kalliope ( ; minor planet designation: 22 Kalliope) is a large M-type asteroid from the asteroid belt discovered by J. R. Hind on 16 November 1852. It is named after Calliope, the Greek Muse of epic poetry. It is orbited by a small moon named Linus. Characteristics Kalliope is somewhat elongated, approximately 166 km in diameter, and slightly asymmetric, as evidenced by resolved images taken with the VLT at the European Southern Observatory. This new diameter, which was measured by observing mutual eclipses of Kalliope and Linus, is 8% smaller than that calculated from IRAS observations. The spectrum of Kalliope is an M-type, indicating that its surface may be partially composed of iron–nickel metal. The asteroid's density is about 3.4 g/cm3. Since the asteroid is likely to be a rubble pile, accounting for a possible porosity of 20–40% leads to the material density of 4.2–5.8 g/cm3, which means that Kalliope is probably made of a mixture of metal with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linus (moon)
(22) Kalliope I Linus is an asteroid moon that orbits the large M-type asteroid 22 Kalliope. It was discovered on August 29, 2001, by astronomers Jean-Luc Margot and Michael E. Brown with the Keck telescope, in Hawaii. Another team also detected the moon with the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope on September 2, 2001. Both telescopes are on Mauna Kea. It received the provisional designation S/2001 (22) 1, until it was named. The naming proposal appeared in the discovery paper and was approved by the International Astronomical Union in July 2003. Although the naming proposal referred to the mythological Linus, son of the muse Calliope and the inventor of melody and rhythm, the name was also meant to honor Linus Torvalds, inventor of the Linux operating system kernel, and Linus van Pelt, a character in the ''Peanuts'' comic strip. With an estimated (17 ± 1 mi) diameter, Linus is very large compared to most asteroid moons, and would be a sizable asteroid by itself. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poetry
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin ''epicus'', which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adjective (''epikos''), from (''epos''), "word, story, poem." In ancient Greek, 'epic' could refer to all poetry in dactylic hexameter (''epea''), which included not only Homer but also the wisdom poetry of Hesiod, the utterances of the Delphic oracle, and the strange theological verses attributed to Orpheus. Later tradition, however, has restricted the term 'epic' to ''heroic epic'', as described in this article. Overview Originating before the invention of writing, primary epics, such as those of Homer, were composed by bards who used complex rhetorical and metrical schemes by which they could memorize the epic as receive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Luc Margot
Jean-Luc Margot (born 1969) is a Belgian-born astronomer and a UCLA professor who specializes in planetary sciences. Career Margot has discovered and studied several binary asteroids with radar and optical telescopes. His discoveries include (87) Sylvia I Romulus, (22) Kalliope I Linus, S/2003 (379) 1, (702) Alauda I Pichi üñëm, and the binary nature of (69230) Hermes. In 2000, he obtained the first images of binary near-Earth asteroids and described formation of the binary by a spin-up process. Margot and his research group have studied the influence of sunlight on the orbits and spins of asteroids, the Yarkovsky and YORP effects. In 2007, Margot and collaborators determined that Mercury has a molten core from the analysis of small variations in the rotation rate of the planet. These observations also enabled a measurement of the size of the core based on a concept proposed by Stan Peale. In 2012, Margot and graduate student Julia Fang analyzed Kepler space tele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks from view (occults) an object in the background. In this general sense, occultation applies to the visual scene observed from low-flying aircraft (or computer-generated imagery) when foreground objects obscure distant objects dynamically, as the scene changes over time. If the closer body does not entirely conceal the farther one, the event is called a ''transit''. Both transit and occultation may be referred to generally as ''occlusion''; and if a shadow is cast onto the observer, it is called an eclipse. The symbol for an occultation, and especially a solar eclipse, is file:Occultation symbol.svg (U+1F775 🝵). Occultations by the Moon The term occultation is most frequently used to describe lunar occultations, those relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Earth's obliquity oscillates between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees on a 41,000-year cycle. Based on a continuously updated formula (here Laskar, 1986, though since 2006 the IMCCE and the IAU recommend the P03 model), Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic Coordinate System
The ecliptic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system commonly used for representing the apparent positions, orbits, and pole orientations of Solar System objects. Because most planets (except Mercury) and many small Solar System bodies have orbits with only slight inclinations to the ecliptic, using it as the fundamental plane is convenient. The system's origin can be the center of either the Sun or Earth, its primary direction is towards the vernal (March) equinox, and it has a right-hand convention. It may be implemented in spherical or rectangular coordinates. Primary direction The celestial equator and the ecliptic are slowly moving due to perturbing forces on the Earth, therefore the orientation of the primary direction, their intersection at the Northern Hemisphere vernal equinox, is not quite fixed. A slow motion of Earth's axis, precession, causes a slow, continuous turning of the coordinate system westward about the poles of the ecliptic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Hydration
In chemistry, mineral hydration is an inorganic chemical reaction which adds water to the crystal structure of a mineral, usually creating a new mineral, usually called a ''hydrate''. In geological terms, the process of mineral hydration is known as ''retrograde alteration'' and is a process occurring in retrograde metamorphism. It commonly accompanies metasomatism and is often a feature of wall rock alteration around ore bodies. Hydration of minerals occurs generally in concert with hydrothermal circulation which may be driven by tectonic or igneous activity. Processes There are two main ways in which minerals hydrate. One is conversion of an oxide to a double hydroxide, as with the hydration of calcium oxide—CaO—to calcium hydroxide—Ca(OH)2, the other is with the incorporation of water molecules directly into the crystalline structure of a new mineral. The later process is exhibited in the hydration of feldspars to clay minerals, garnet to chlorite, or kyanite to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
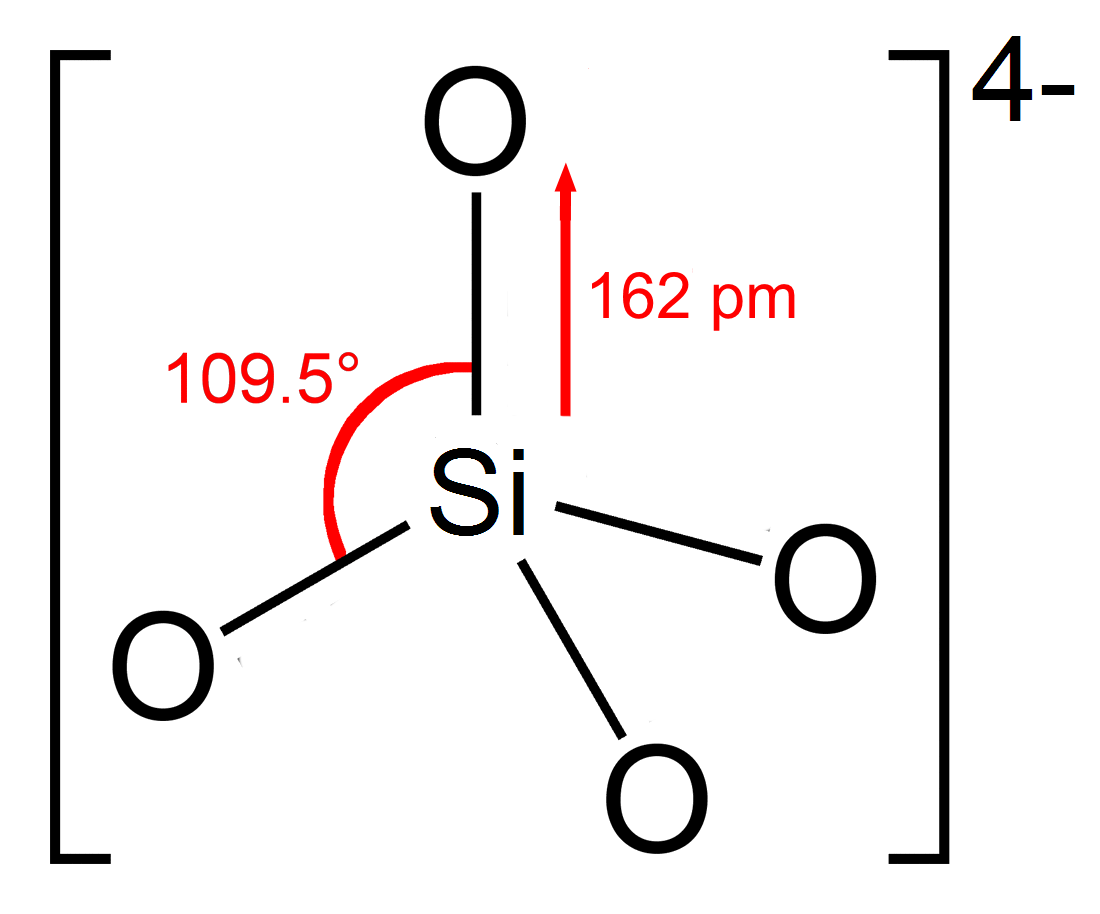
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubble Pile
In astronomy, a rubble pile is a celestial body that is not a monolith, consisting instead of numerous pieces of rock that have coalesced under the influence of gravity. Rubble piles have low density because there are large cavities between the various chunks that make them up. The asteroids Bennu and Ryugu have a measured bulk density which suggests a rubble pile internal structure. Many comets and most smaller minor planets (<10 km in diameter) are thought to be composed of coalesced rubble. Minor planets  Most smaller s are thought to be rubble piles.
Rubble piles fo ...
Most smaller s are thought to be rubble piles.
Rubble piles fo ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Southern Observatory
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 member states for ground-based astronomy. Created in 1962, ESO has provided astronomers with state-of-the-art research facilities and access to the southern sky. The organisation employs about 730 staff members and receives annual member state contributions of approximately €162 million. Its observatories are located in northern Chile. ESO has built and operated some of the largest and most technologically advanced telescopes. These include the 3.6 m New Technology Telescope, an early pioneer in the use of active optics, and the Very Large Telescope (VLT), which consists of four individual 8.2 m telescopes and four smaller auxiliary telescopes which can all work together or separately. The Atacama Large Millimeter Array observes the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |